Unveiling the Mysteries: 10 Fascinating Facts About Mars
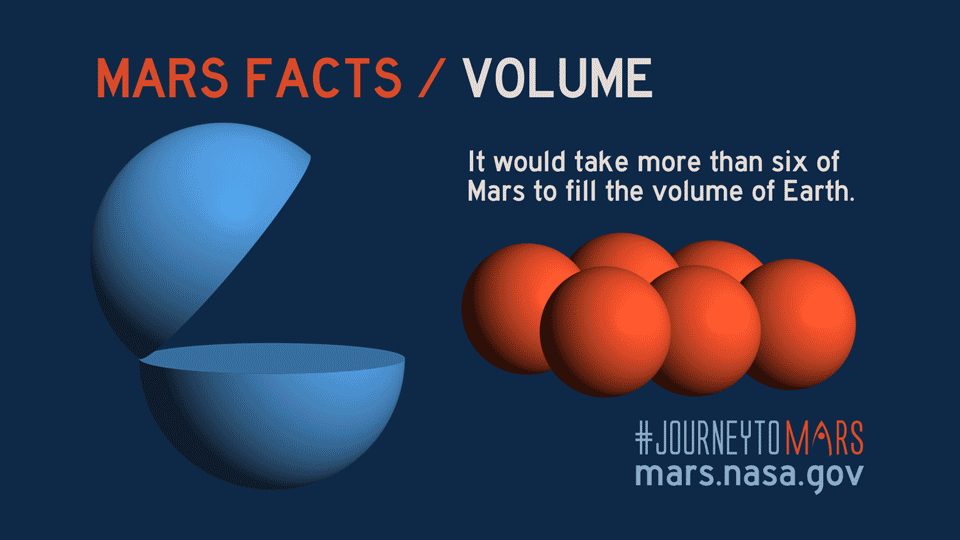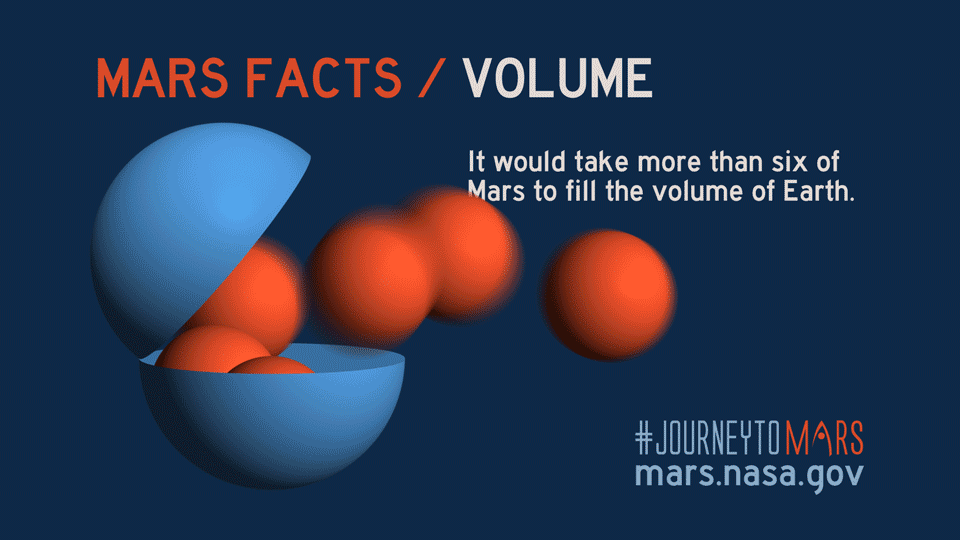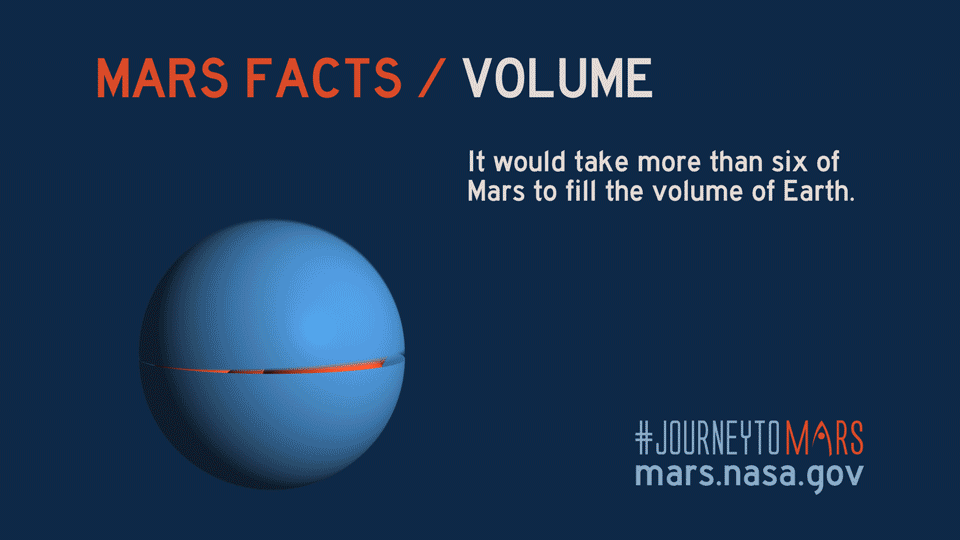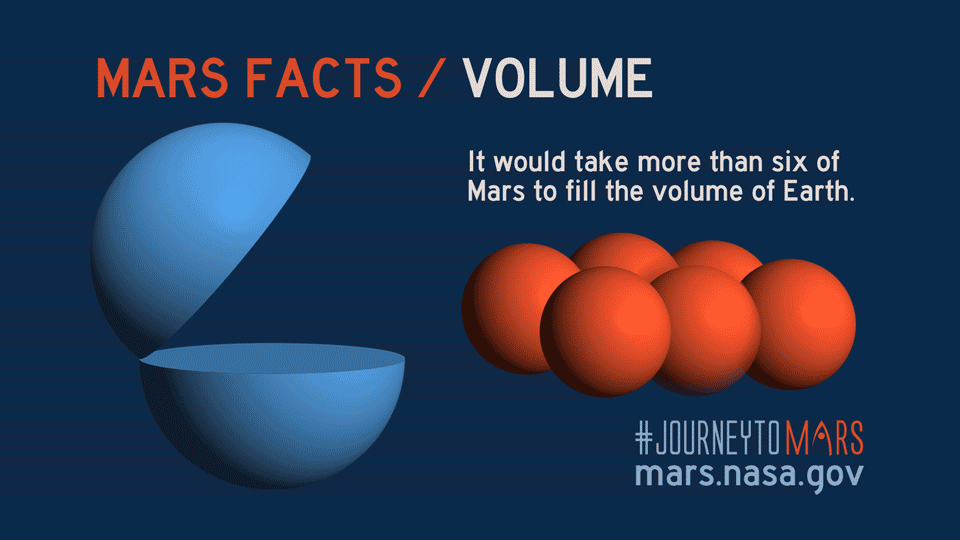
Introduction
Gazing up at the night sky, it's hard not to be captivated by the mysterious allure of Mars, the crimson beacon that has sparked the curiosity of dreamers and scientists for centuries. As the fourth planet from the sun, Mars has long been the subject of speculation, exploration, and even the backdrop for countless tales of adventure and intrigue. But what lies beneath its rusty surface and thin atmosphere that makes it such a compelling subject for exploration? From its towering volcanoes to its enigmatic moons, Mars is a planet of extremes and enigmas, holding secrets that could redefine our understanding of the solar system and potentially life itself.
| Quick Info: Mars |
|---|
| Position from Sun: 4th |
| Diameter: 6,779 km |
| Moons: Phobos and Deimos |
| Atmosphere: Thin, mostly CO2 |
| Surface Temperature: -87 to -5°C |
The Red Planet's Physical Characteristics
Mars is famously known as the Red Planet, a moniker derived from its distinct rusty hue. This characteristic color is due to iron oxide, or rust, on its surface. Unlike Earth, Mars' atmosphere is thin and composed primarily of carbon dioxide, with traces of nitrogen and argon. This composition not only gives Mars its reddish appearance but also contributes to its cold and harsh environment. The thin atmosphere means that Mars lacks the protective shield that Earth has, allowing more radiation from the sun to reach its surface.
Mars' Iconic Landmarks
Olympus Mons
Mars is home to some of the solar system's most extraordinary features, including Olympus Mons, the largest volcano known. Standing at about 22 kilometers high, nearly three times the height of Mount Everest, Olympus Mons is a shield volcano, characterized by its broad, gently sloping sides. Its immense size is a testament to the volcanic activity that once shaped Mars' surface.
Valles Marineris
Equally impressive is Valles Marineris, a massive canyon system that stretches over 4,000 kilometers, roughly the distance from New York to Los Angeles. This vast chasm cuts deep into the Martian surface, providing a glimpse into the planet's geological past. The origins of Valles Marineris remain a mystery, with theories suggesting it was formed by tectonic processes or the collapse of subterranean magma chambers.
The Search for Life on Mars
The question of whether life exists, or once existed, on Mars has driven numerous scientific missions. Early Mars missions focused on detecting signs of life, primarily through the search for water, as it is essential for life as we know it. The discovery of ancient riverbeds and polar ice caps suggests that liquid water once flowed on Mars. Current theories propose that microbial life could exist beneath the surface, where conditions might be more stable. Ongoing missions by NASA's Perseverance rover and the European Space Agency aim to uncover more evidence of past or present life.
Mars' Climate and Weather Patterns
Mars experiences extreme temperatures and weather patterns, with temperatures ranging from -87°C to -5°C. The planet's thin atmosphere and lack of a significant magnetic field contribute to these extremes. Dust storms are a common weather event on Mars, sometimes enveloping the entire planet for weeks. These storms can obscure the surface and pose challenges for solar-powered missions. Despite its harsh climate, Mars shares similarities with Earth, such as polar ice caps and seasonal changes, offering insights into potential future colonization.
The Mysteries of Mars' Moons
Mars is orbited by two small moons, Phobos and Deimos. These irregularly shaped celestial bodies are thought to be captured asteroids, although their exact origins remain uncertain. Phobos, the larger of the two, is gradually spiraling inward and may eventually collide with Mars or break apart to form a ring. The composition and behavior of these moons continue to intrigue scientists, providing clues about the early solar system.
Mars' Exploration History
Human fascination with Mars has led to numerous exploratory missions. The first successful flyby was by NASA's Mariner 4 in 1965, which provided the first close-up images of Mars. Since then, a fleet of rovers and orbiters, including the famous Curiosity and Perseverance rovers, have been deployed to study the planet's surface and atmosphere. Future missions, such as the Mars Sample Return mission, aim to bring Martian soil and rocks back to Earth for detailed analysis, further unraveling the mysteries of Mars.
Mars in Popular Culture
Mars has captivated human imagination for centuries, serving as the setting for countless works of fiction. From H.G. Wells' "The War of the Worlds" to modern films like "The Martian," Mars has been depicted as a place of adventure and intrigue. This cultural fascination reflects humanity's enduring curiosity about exploring new frontiers and the possibility of life beyond Earth. The idea of colonizing Mars has also gained traction, inspiring discussions about human resilience and adaptability.
Mars' Potential for Human Exploration
The prospect of sending humans to Mars presents both challenges and opportunities. The harsh environment, distance from Earth, and technological demands pose significant obstacles. However, advancements in space travel and international collaboration are paving the way for potential manned missions. Organizations like NASA and SpaceX have proposed timelines for human exploration, with goals of establishing a sustainable presence on Mars. These efforts underscore the importance of Mars as a stepping stone for deeper space exploration and the future of humanity.
Conclusion
Mars, with its vibrant history and enigmatic features, continues to be a focal point of scientific inquiry and human imagination. From its towering volcanoes and vast canyons to the tantalizing possibility of life, Mars offers a wealth of knowledge and inspiration. As we continue to explore and study the Red Planet, we not only seek to understand our place in the solar system but also to pave the way for future generations to reach for the stars. The journey to Mars is not just about scientific discovery; it's about the enduring human spirit of exploration and the quest to uncover the unknown.